 Java IO
Java IO
# bio
java.io和java.net包,代码简单直观,同步/阻塞IO,一个连接需要一个处理线程,如果是几百个连接的应用,不会有什么问题,如果连接数比较多,会产生过多线程,占用较多系统资源和频繁的上下文切换。
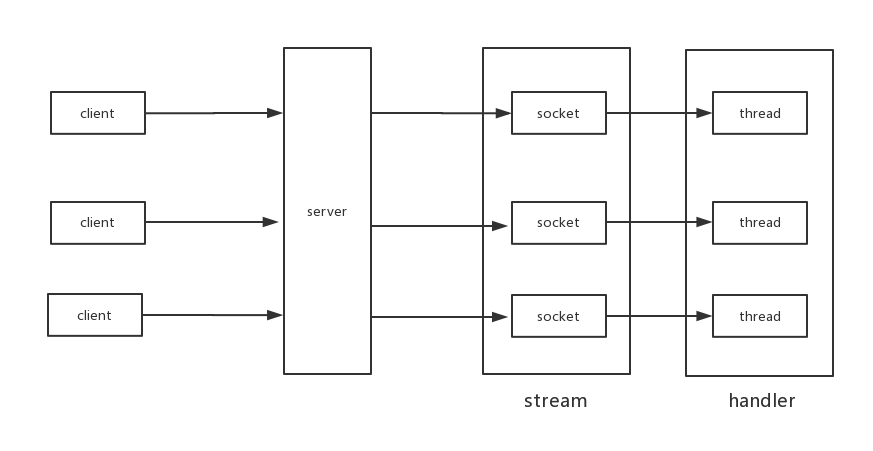
socket io server经典处理模型
示例代码
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class IOServer extends Thread {
private volatile boolean running = true;
private ServerSocket serverSocket;
private ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
public void stopServer() {
this.running = false;
if (serverSocket != null) {
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
pool.shutdown();
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// port=0,表示随机监听一个空闲端口
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(0);
System.out.println("server started, listing port: " + serverSocket.getLocalPort());
while (running) {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
RequestHandler handler = new RequestHandler(socket);
pool.execute(handler);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
stopServer();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new IOServer().start();
}
private static class RequestHandler extends Thread {
private volatile boolean alive = true;
private Socket socketClient;
private Scanner scanner;
private PrintStream out;
RequestHandler(Socket socketClient) {
this.socketClient = socketClient;
try {
this.scanner = new Scanner(socketClient.getInputStream());
this.scanner.useDelimiter("\n");
this.out = new PrintStream(socketClient.getOutputStream());
System.out.println("client connectd: " + socketClient.getInetAddress().getHostAddress());
this.out.println("hello");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void close() {
alive = false;
scanner.close();
out.close();
if (!socketClient.isClosed()) {
try {
socketClient.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (alive) {
if (socketClient.isClosed()) {
System.out.println("client closed");
this.close();
return;
}
if (this.scanner.hasNext()) {
String data = this.scanner.next().trim();
if ("".equals(data)) {
continue;
}
if ("exit".equalsIgnoreCase(data)) {
out.println("bye...");
this.close();
} else {
System.out.printf("receive: %s \n", data);
out.printf("receive: %s \n", data);
}
}
}
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
使用telnet连接server测试
# 连接客户端
~ telnet 127.0.0.1 58605
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
hello
# 向服务端发送数据
world
# 收到服务器响应数据
receive: world
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# nio
java.nio包,jdk1.4+版本。api复杂,使用不当容易出现问题。同步/非阻塞IO,真正的IO操作还是同步的,一个请求占用一个处理线程。核心组件Selector、Channel、Buffer,单个server通常能处理上万个连接
nio server处理模型

参考教程:
- http://ifeve.com/java-nio-all (opens new window)
- http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-nio/index.html (opens new window)
- http://rox-xmlrpc.sourceforge.net/niotut/ (opens new window)
- http://www.importnew.com/24794.html (opens new window)
- http://www.importnew.com/28007.html (opens new window)
java.nio.channels.SelectionKey
| 事件 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| OP_ACCEPT | 请求在接受新连接并创建 Channel 时获得通知 |
| OP_CONNECT | 请求在建立一个连接时获得通知 |
| OP_READ | 请求当数据已经就绪,可以从 Channel 中读取时获得通知 |
| OP_WRITE | 请求当可以向 Channel 中写更多的数据时获得通知。这处理了套接字缓冲区被完 全填满时的情况,这种情况通常发生在数据的发送速度比远程节点可处理的速度更 快的时候 |
示例代码
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class NIOServer extends Thread {
private int port;
private ServerSocketChannel serverChannel;
private Selector selector;
private ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
private Map<SocketChannel, Queue<ByteBuffer>> pendingData = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(10);
public NIOServer(int port) throws IOException {
this.port = port;
this.selector = this.initSelector();
}
private Selector initSelector() throws IOException {
Selector socketSelector = SelectorProvider.provider().openSelector();
this.serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
InetSocketAddress isa = new InetSocketAddress(this.port);
serverChannel.socket().bind(isa);
serverChannel.register(socketSelector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("server started, listing port: " + port);
return socketSelector;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
if (this.selector.select() < 1) {
continue;
}
Iterator selectedKeys = this.selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (selectedKeys.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) selectedKeys.next();
selectedKeys.remove();
if (!key.isValid()) {
continue;
}
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
this.accept(key);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
this.read(key);
} else if (key.isWritable()) {
this.write(key);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void accept(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 响应数据消息队列
Queue<ByteBuffer> queue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(10);
pendingData.put(socketChannel, queue);
socketChannel.register(this.selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
private void read(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
this.readBuffer.clear();
int numRead;
try {
numRead = socketChannel.read(this.readBuffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
closeClient(key);
return;
}
if (numRead == -1) {
closeClient(key);
return;
}
String data = new String(readBuffer.array(), 0, numRead).trim();
// 退出指令
if ("exit".equalsIgnoreCase(data)) {
closeClient(key);
return;
}
pendingData.get(socketChannel).add(Charset.defaultCharset().encode("receive: " + data + "\n"));
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
private void write(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
Queue<ByteBuffer> queue = pendingData.get(socketChannel);
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ByteBuffer buffer = queue.poll();
while (buffer != null) {
socketChannel.write(buffer);
buffer = queue.poll();
}
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
}
private void closeClient(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
key.channel().close();
key.cancel();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
new NIOServer(6666).start();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
# nio2(aio)
jdk1.7+版本,api复杂,异步非阻塞IO,IO操作完全交给操作系统。采用事件通知回调机制,其read和write方法均是异步。
实例代码
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousChannelGroup;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class AIOServer {
private int port;
private ExecutorService executorService;
private AsynchronousChannelGroup threadGroup;
public AsynchronousServerSocketChannel asynServerSocketChannel;
public AIOServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public AIOServer start() {
try {
executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
threadGroup = AsynchronousChannelGroup.withCachedThreadPool(executorService, 1);
asynServerSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(threadGroup);
asynServerSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
System.out.println("server start , port : " + port);
asynServerSocketChannel.accept(this, new AcceptHandler());
return this;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void sync() {
synchronized (this) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
static class AcceptHandler implements CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, AIOServer> {
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel, AIOServer attachment) {
attachment.asynServerSocketChannel.accept(attachment, this);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
clientChannel.read(buffer, buffer, new LogicHandler(clientChannel));
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, AIOServer attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
}
static class LogicHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> {
private AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel;
public LogicHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel) {
this.clientChannel = clientChannel;
}
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
System.out.println("result: " + result);
if (!clientChannel.isOpen() || result < 0) {
System.out.println("client close");
this.close();
return;
}
attachment.flip();
String data = new String(attachment.array()).trim();
if ("exit".equalsIgnoreCase(data)) {
this.close();
}
write(clientChannel, "receive: " + data + "\r\n");
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
clientChannel.read(buffer, buffer, this);
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
private void write(AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel, String response) {
try {
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buf.put(response.getBytes());
buf.flip();
clientChannel.write(buf).get();
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void close() {
try {
clientChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AIOServer server = new AIOServer(6666);
server.start().sync();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
# 总结
| - | BIO | NIO | AIO |
|---|---|---|---|
| 阻塞/非阻塞 | 阻塞 | 非阻塞 | 非阻塞 |
| 同步/异步 | 同步 | 同步 | 异步 |
| 性能 | 低 | 高 | 非常高 |
| 线程比(server:client) | 1:1 | 1:N | 0:N |
| 吞吐 | 低 | 高 | 高 |
# 同步与异步IO的区别
进程IO操作步骤:
- 进程向操作系统请求数据
- 操作系统把数据加载到内核的缓冲区
- 操作系统把内核的缓冲区拷贝到进程的缓冲区
- 进程从缓冲区获得数据
同步与异步IO的区别在于,操作系统操作缓冲区的时候(2、3),应用线程是否处于挂起状态(可以处理其他逻辑)。
# 阻塞与非阻塞区别
进程在开始IO操作之前,需要有一些准备工作,例如网络等待,在数据没有就绪前实际上还没有开始IO操作。
- 阻塞:在真正IO操作开始前,线程处于阻塞状态,不能处理其他逻辑。
- 非阻塞:在真正IO操作前,不需要等待,此时线程可以处理其他逻辑。
Last Updated: 2024/04/23, 01:30:37